P53 Gene Cancer
P53 is the most frequently mutated gene in human cancer 37. When the p53 gene become mutated it gives rise to a stable mutant protein whose accumulation is regarded as a hallmark of cancer cells.
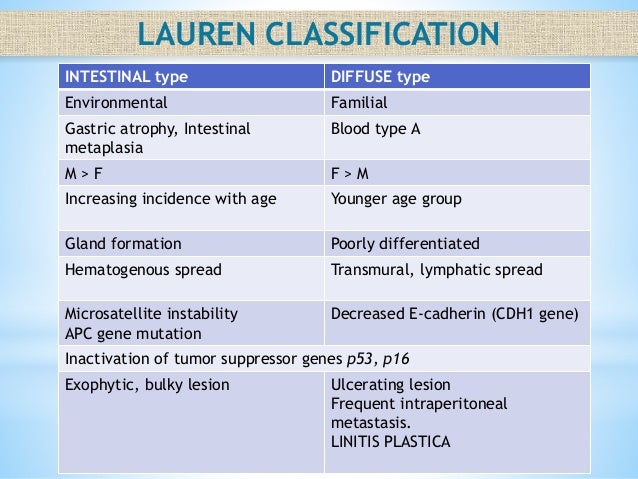 Gastric Cancer Carcinoma Management 21 638 Jpg 638 479 Pixels Gastric Cancer Gastric Carcinoma Lymphatic
Gastric Cancer Carcinoma Management 21 638 Jpg 638 479 Pixels Gastric Cancer Gastric Carcinoma Lymphatic
The click learn presents different types of genes that when mutated contribute to cancer including oncogenes tumor suppressor genes and dna repair genes.

P53 gene cancer. This tumor suppressor and transcription factor regulates several genes that protect against neoplastic transformation including those involved in the modulation of the cell cycle dna repair apoptosis senescence angiogenesis and metabolism 38. The p53 gene tp53 is a gene that is mutated in many cancers and is the most common gene mutation found in cancer cells. Emerging evidence from laboratories and clinical trials shows that some small molecule inhibitors exert anti cancer effect via reactivation and restoration of p53 function.
P53 gene mutation have several different effects on the activity of the gene depending on the location of the alteration. This tutorial describes the structure and function of the p53 protein how its activity is regulated in cells and how mutant versions of p53 can lead to cancer. The gene is a type of tumor suppressor gene that codes for a protein that inhibits the development and growth of tumors.
P53 functions as a negative regulator of cell growth and alterations in the gene lead to loss of this negative growth regulation and more rapid cell proliferation. Tumor protein p53 also known as p53 cellular tumor antigen p53 uniprot name the guardian of the genome phosphoprotein p53 tumor suppressor p53 antigen ny co 13 or transformation related protein 53 trp53 is any isoform of a protein encoded by homologous genes in various organisms such as tp53 humans and trp53 mice. Mutation in the p53 gene.
Alterations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene are the most common genetic changes found so far in breast cancer suggesting that the gene plays a central role in the development of the disease. Tumor suppressor p53 protein is a transcription factor inducing cell cycle arrest senescence and apoptosis under cellular stress. These mutant p53 proteins not only lose their tumor suppressive activities but often gain additional oncogenic functions as a result cells become abnormal in terms of growth and survival advantages.
 P53 And Dna Damage Recent Discoveries Mitochondrial Dna
P53 And Dna Damage Recent Discoveries Mitochondrial Dna
 Login To Schoology Oncology Rn Schoology Tumor
Login To Schoology Oncology Rn Schoology Tumor
 Tj The P53 Pathway Responds To Stresses That Can Disrupt The Fidelity Of Dna Replication And Cell Division A Stress Signal Is Transmitted To The P53 Protein B
Tj The P53 Pathway Responds To Stresses That Can Disrupt The Fidelity Of Dna Replication And Cell Division A Stress Signal Is Transmitted To The P53 Protein B
 Primary Information Of P53 Gene Dna Repair Biochemistry Physiology
Primary Information Of P53 Gene Dna Repair Biochemistry Physiology
 The P53 Gene And Cancer Hhmi S Biointeractive
The P53 Gene And Cancer Hhmi S Biointeractive
 Possible Problems With Stem Cell Transplant Harvard Researchers Found That As Stem Cell Lines Grow In A Lab Dish The Stem Cell Transplant Cell Line Stem Cells
Possible Problems With Stem Cell Transplant Harvard Researchers Found That As Stem Cell Lines Grow In A Lab Dish The Stem Cell Transplant Cell Line Stem Cells
 Https D1j63owfs0b5j3 Cloudfront Net Tutorial Finalimage 933 1461094247114 Png Tutorial Methylation Amino Acids
Https D1j63owfs0b5j3 Cloudfront Net Tutorial Finalimage 933 1461094247114 Png Tutorial Methylation Amino Acids
 Qiagen Geneglobe Pathways P53 Signaling P53 Is A Tumour Suppressor Protein That Regulates The Expression Of A Wide Variety Cell Cycle Pathways Dna Repair
Qiagen Geneglobe Pathways P53 Signaling P53 Is A Tumour Suppressor Protein That Regulates The Expression Of A Wide Variety Cell Cycle Pathways Dna Repair
 Meet Gene P53 Medical School Studying Biochemistry Biology
Meet Gene P53 Medical School Studying Biochemistry Biology
 Tj The P53 Pathway Responds To Stresses That Can Disrupt The Fidelity Of Dna Replication And Cell Division A Stress Sig Dna Replication Cell Cycle Dna Repair
Tj The P53 Pathway Responds To Stresses That Can Disrupt The Fidelity Of Dna Replication And Cell Division A Stress Sig Dna Replication Cell Cycle Dna Repair
 Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Mapk Life Technologies Biochemistry Signal Transduction Plant Science
Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Mapk Life Technologies Biochemistry Signal Transduction Plant Science
 Usmle Step 1 Oncogenes Tumor Suppressor Genes Tumor Gene Suppressor
Usmle Step 1 Oncogenes Tumor Suppressor Genes Tumor Gene Suppressor
 Cell Cycle Copy Cancer Genetics Cell Biology Cell Cycle
Cell Cycle Copy Cancer Genetics Cell Biology Cell Cycle
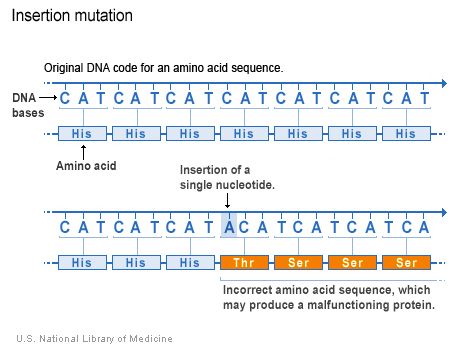 Types Of Gene Mutations Genetics Home Reference Dna Mắt
Types Of Gene Mutations Genetics Home Reference Dna Mắt
 P53 Evolution Tumor Suppressor Gene That Helps In Cell Cycle Signal Transduction Dna Replication Cell Cycle
P53 Evolution Tumor Suppressor Gene That Helps In Cell Cycle Signal Transduction Dna Replication Cell Cycle
 P53 Signaling Pathway Malignant Tumor Cell Division Dna Repair
P53 Signaling Pathway Malignant Tumor Cell Division Dna Repair



Comments
Post a Comment